Chinese Medical Sciences Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 79-90.doi: 10.24920/004327
• Guideline and Consensus • Next Articles
A Chinese Multi-Specialty Delphi Consensus to Optimize RAASi Usage and Hyperkalaemia Management in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Heart Failure
Ming-Hui Zhao1, *( ), Wei Chen2(
), Wei Chen2( ), Hong Cheng3(
), Hong Cheng3( ), Bi-Cheng Liu4(
), Bi-Cheng Liu4( ), Zhi-Guo Mao5(
), Zhi-Guo Mao5( ), Zhuang Tian6(
), Zhuang Tian6( ), Gang Xu7(
), Gang Xu7( ), Jing-Min Zhou9(
), Jing-Min Zhou9( )
)
- 1Renal Division, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
2Department of Nephrology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510080, China
3Department of Nephrology, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100029, China
4Department of Nephrology, Southeast University Zhongda Hospital, Nanjing 210009, China
5Department of Nephrology, Shanghai Changzheng Hospital, Shanghai 200003, China
6Department of Cardiology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing 100730, China
7Renal Division, Tongji Medical College of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, China
8Department of Cardiology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China
-
Received:2023-12-05Accepted:2024-04-08Published:2024-06-30Online:2024-06-07 -
Contact:*mhzhao@bjmu.edu.cn .
Cite this article
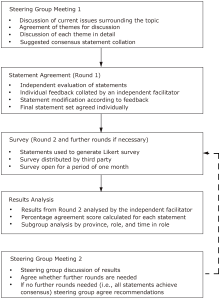
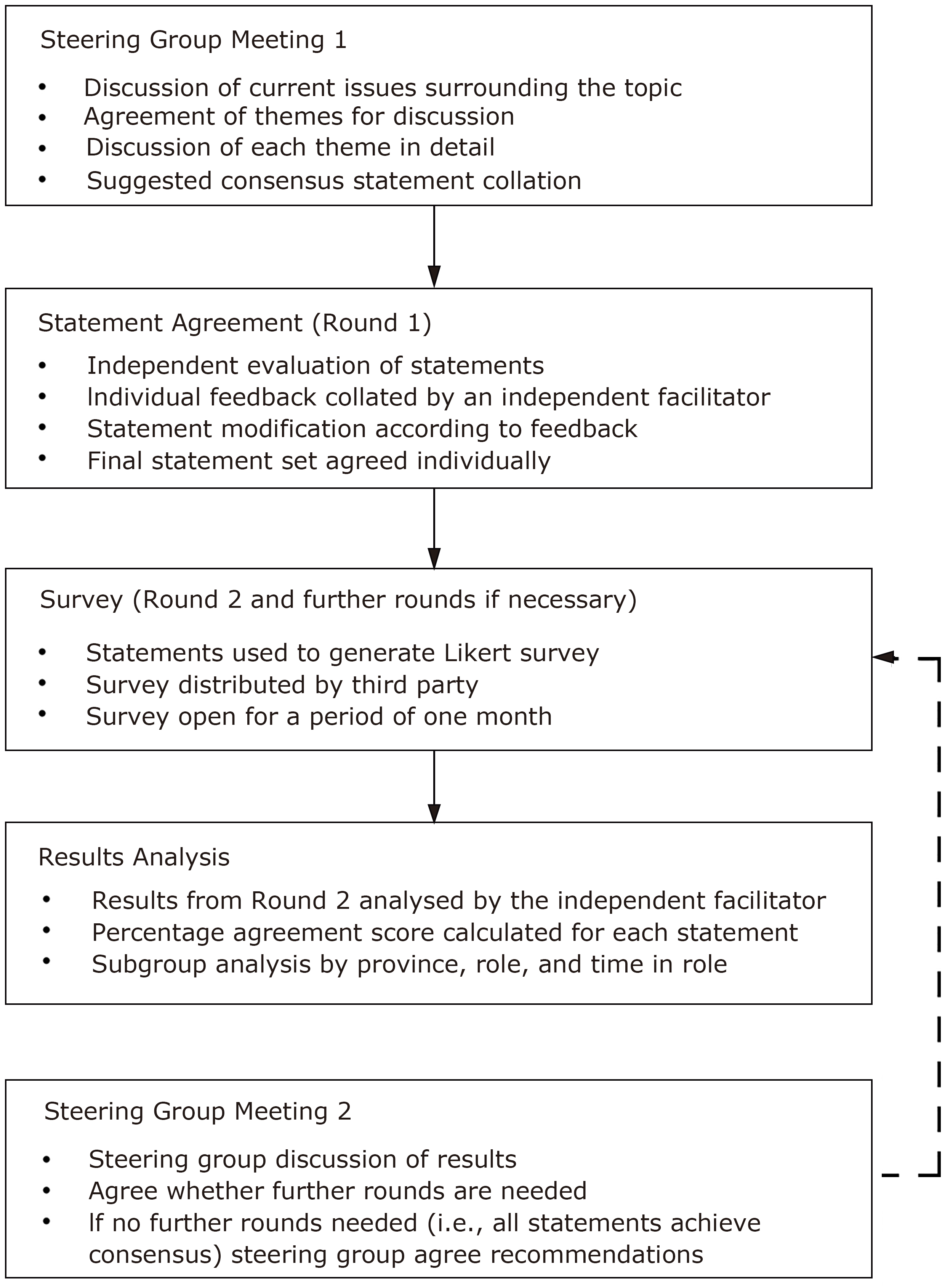
Ming-Hui Zhao, Wei Chen, Hong Cheng, Bi-Cheng Liu, Zhi-Guo Mao, Zhuang Tian, Gang Xu, Jing-Min Zhou. A Chinese Multi-Specialty Delphi Consensus to Optimize RAASi Usage and Hyperkalaemia Management in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Heart Failure[J].Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2024, 39(2): 79-90.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
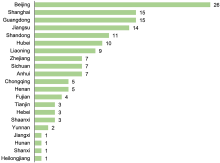
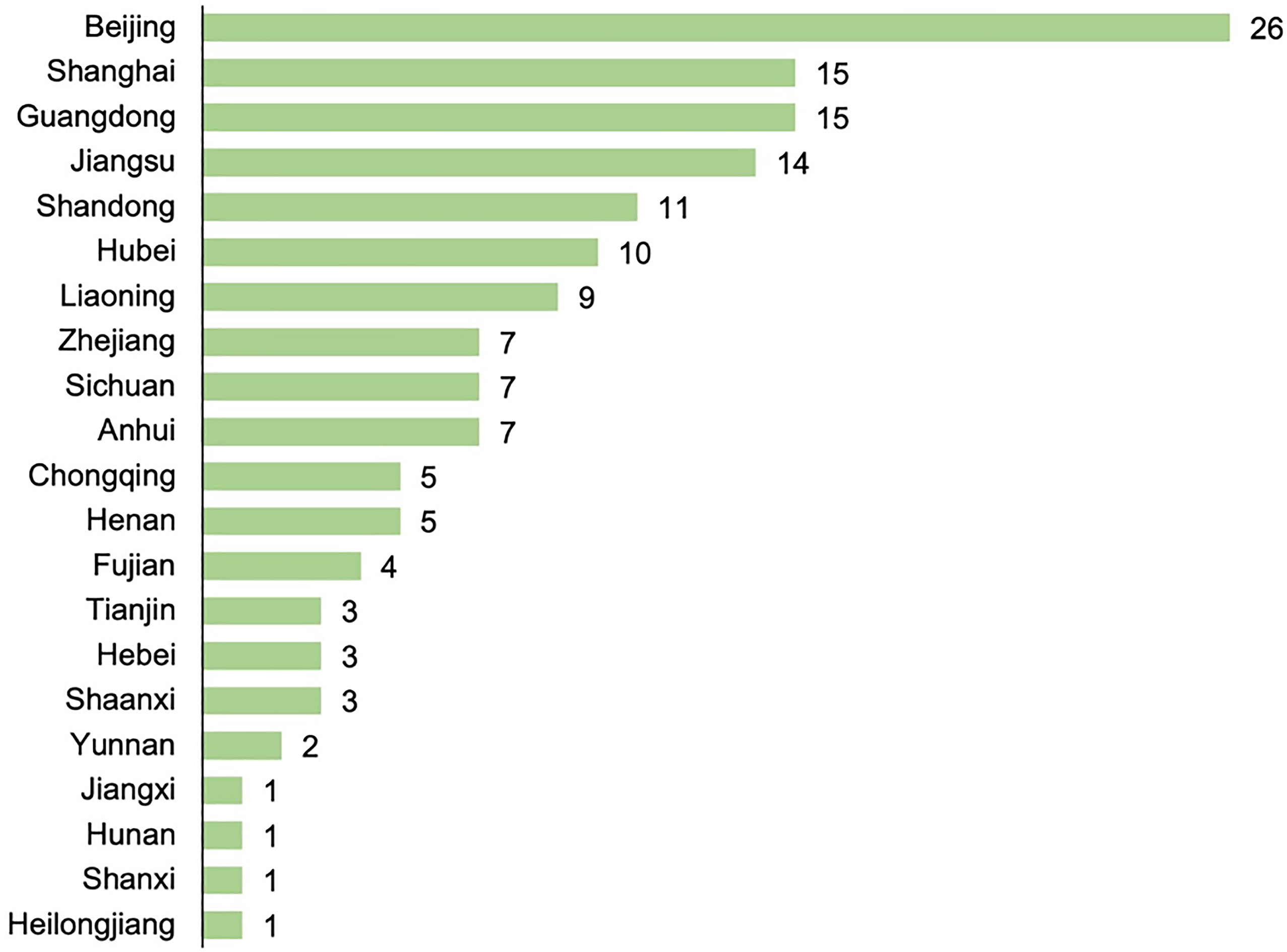
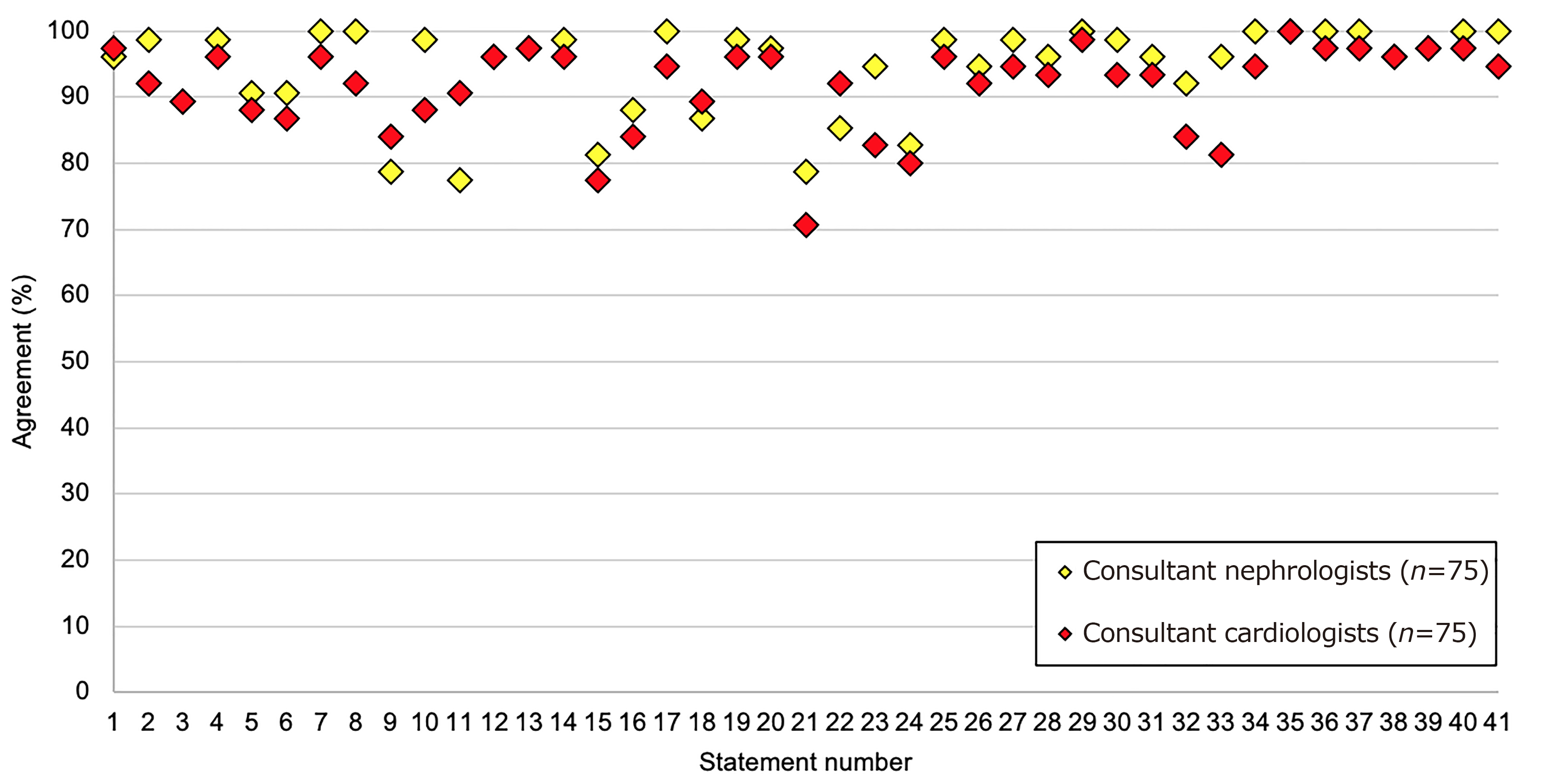
Table 1.
Consensus agreement by statement of five topics on RAASi usage and hyperkalaemia management"
| No. | Statements | Agreement |
|---|---|---|
| Topic A. Risk factors and risk stratification for managing hyperkalaemia in cardiorenal patients | ||
| 1. | Patients with chronic kidney disease, heart failure, or diabetes are at increased risk of hyperkalaemia | 97% |
| 2. | Patients on RAASi and MRA treatments are at increased risk of hyperkalaemia | 95% |
| 3. | Cardiorenal patients should have their serum potassium levels tested at least every 6 months or more according to disease severity | 89% |
| 4. | Cardiorenal patients undergoing RAASi up-titration should have their serum potassium levels tested at least every two weeks during the up-titration period and monitored routinely thereafter | 97% |
| 5. | Patients with CKD stage 4/5 should have their serum potassium levels tested at least every 3 months | 89% |
| 6. | Patients who have an episode of hyperkalaemia should have their serum potassium levels tested two weeks later and at least every 3 months thereafter | 89% |
| Topic B. Prevention of hyperkalaemia for at-risk cardiorenal patients | ||
| 7. | For those patients with a known history of hyperkalaemia preventing optimization of RAASi therapy, a novel potassium binder can be used to enable RAASi optimization | 98% |
| 8. | For those patients at risk of hyperkalaemia using RAASi therapy, advice about dietary considerations and the impact on potassium levels should be provided | 96% |
| 9. | While a low potassium diet is commonly advised, this approach may be counter to a heart healthy diet that is beneficial to cardiorenal patients | 81% |
| 10. | Low potassium diets can be difficult to follow, especially during certain seasons where different fruits are more readily available | 93% |
| 11. | Advising a low potassium diet to control hyperkalaemia is increasingly controversial: the evidence for the effectiveness of a low-potassium diet is not strong | 84% |
| Topic C. Correction of hyperkalaemia for at-risk cardiorenal patients with the use of potassium-lowering therapy | ||
| 12. | Hyperkalaemia should be recognized as a predictable, treatable, and manageable side effect of optimal heart failure/chronic kidney disease therapy | 96% |
| 13. | Optimizing and maintaining RAASi therapy provides better outcomes for cardiorenal patients including morbidity and mortality | 97% |
| 14. | In practice, the occurrence of hyperkalaemia may lead to the down-titration or discontinuation of RAASi therapy | 97% |
| 15. | When managing mild-to-moderate hyperkalaemia in cardiorenal patients, RAASi therapy should be maintained due to the cardioprotective benefit in this patient type | 79% |
| 16. | A goal for the management of cardiorenal patients should be to utilise the maximum recommended dose of RAASi therapy | 86% |
| 17. | Action to manage hyperkalaemia should be taken when the serum potassium level exceeds 5.0 mmol/L | 97% |
| 18. | RAASi use should not be de-escalated or discontinued due to hyperkalaemia unless alternative methods of hyperkalaemia management have been optimised, including initiation of potassium binder therapy | 88% |
| 19. | Novel potassium binders enable guideline recommended RAASi dosing and the proven benefits that they bring to patients | 97% |
| 20. | When potassium levels exceed 6.5 mmol/L, RAASi treatment down-titration, suspension, or cessation should be considered | 97% |
| 21. | When treating cardiorenal patients, permanent discontinuation of RAASi therapy should be considered a last resort strategy | 75% |
| 22. | Where disease-modifying therapy has been reduced or ceased due to hyperkalaemia, it should be reinstated once normokalaemia is achieved | 89% |
| 23. | Prolonged use of SPS should be avoided due to the association with severe gastrointestinal side effects, including bowel necrosis | 89% |
| 24. | Prolonged use of SPS should be avoided due to its poor palatability and poor patient acceptance | 81% |
| Topic D. Cross-specialty alignment (cardiology & nephrology) | ||
| 25. | Continuity of care is important in the management of hyperkalaemia | 97% |
| 26. | Significant variation in approach to cardiorenal diseases and hyperkalaemia management in China leads to variable patient outcomes | 93% |
| 27. | There is a need for a consistent and agreed understanding of hyperkalaemia management within the hospital setting, especially between cardiology & nephrology | 97% |
| 28. | Cardiology and nephrology guidelines should contain aligned recommendations for the management of hyperkalaemia | 95% |
| 29. | Patients with cardiorenal comorbidities should be managed by a MDT with an agreed management plan | 99% |
| 30. | Cross-specialty alignment can enable optimal doses of disease-modifying drugs (e.g., RAASi) to be maintained | 96% |
| 31. | Primary care is an important component of the MDT for the management of cardiorenal patients | 95% |
| 32. | Endocrinology is an important component of the MDT for the management of cardiorenal patients | 88% |
| 33. | Emergency care is an important component of the MDT for the management of cardiorenal patients | 89% |
| 34. | Before making a treatment decision regarding down-titration or cessation of a disease-modifying therapy (e.g., RAASi), primary care should refer to a specialist cardiologist or nephrologist | 97% |
| Topic E. Education of clinicians and patients | ||
| 35. | Up-to-date education on the management of hyperkalaemia and guidelines for RAASi therapy is needed | 100% |
| 36. | Structured education of healthcare providers (HCPs) on routine serum potassium testing and hyperkalaemia management improves patient outcomes | 99% |
| 37. | Education for patients at risk of hyperkalaemia improves their outcomes | 99% |
| 38. | Education of hyperkalaemia management is best delivered by cardiology or nephrology specialists | 96% |
| 39. | Education of non-specialist HCPs (e.g., primary care physicians, emergency physicians, endocrinology physicians, dialysis centre nurses) regarding hyperkalaemia improves patient outcomes | 97% |
| 40. | Patients need to understand the consequences of hyperkalaemia and how to avoid it through lifestyle modification and appropriate use of potassium-lowering therapies | 99% |
| 41. | Patients should be aware of the potential impact that herbal medicines may have on the risk of hyperkalaemia | 97% |
| 1. |
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes KDIGO Diabetes Work Group. KDIGO 2022 clinical practice guideline for diabetes management in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2022; 102 (5S): S1-S127. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.06.008.
pmid: 36272764 |
| 2. | Expert Group on Kidney Clinical Quality Control Center in Shanghai. Guidelines for early screening, diagnosis, and prevention of chronic kidney disease (2022 edition). Chin J Nephrol 2022; 38(5): 453-64. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441217-20210819-00067. |
| 3. |
van de Wouw J, Broekhuizen M, Sorop O, et al. Chronic kidney disease as a risk factor for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a focus on microcirculatory factors and therapeutic targets. Front Physiol 2019; 10: 1108. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01108.
pmid: 31551803 |
| 4. |
Thomas MC, Cooper ME, Zimmet P. Changing epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and associated chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 2016; 12(2): 73-81. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2015.173.
pmid: 26553517 |
| 5. |
McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail 2022; 24(1): 4-131. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2333.
pmid: 35083827 |
| 6. | Wang H, Chai K, Du M, et al. Prevalence and incidence of heart failure among urban patients in China: a national population-based analysis. Circ Heart Fail 2021; 14(10): e008406. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.121.008406. |
| 7. |
Clase CM, Carrero JJ, Ellison DH, et al. Potassium homeostasis and management of dyskalemia in kidney diseases: conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int 2020; 97(1): 42-61. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2019.09.018.
pmid: 31706619 |
| 8. | Simon LV, Hashmi MF, Farrell MW. Hyperkalemia. [Updated 2022 Oct 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 January. |
| 9. | Bian J, Zuo L, Zhao H, et al. Epidemiology and treatment pattern of hyperkalemia among outpatients in China: a descriptive study using an administrative database in China. Chin J Blood Purif 2020; 19(11): 726-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4091.2020.11.002. (Chinese) |
| 10. |
Kanda E, Rastogi A, Murohara T, et al. Clinical impact of suboptimal RAASi therapy following an episode of hyperkalemia. BMC Nephrol 2023; 24(1): 18. doi: 10.1186/s12882-022-03054-5.
pmid: 36658531 |
| 11. | Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes KDIGO Diabetes Work Group. KDIGO 2020 clinical practice guideline for the management of blood pressure in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2020; 98(4S): S1-S115. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.06.019. |
| 12. | Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes KDIGO Blood Pressure Work Group. KDIGO 2021 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Blood Pressure in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int 2021; 99(3S): S1-S87. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.11.003. |
| 13. |
Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2022; 145(18):e895-e1032. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001063.
pmid: 35363499 |
| 14. | Chinese Society of Nephrology. Guidelines for early screening, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of chronic kidney disease (2022 Edition). Chin J Nephrol 2022; 38(5): 453-64. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441217-20210819-00067. (Chinese) |
| 15. | Chinese Society of Nephrology. Guidelines for hypertension management in patients with chronic kidney disease in China (2023). Chin J Nephrol 2023; 39(1): 48-80. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441217-20220630-00650. (Chinese) |
| 16. | Heart Failure Group of Cardiovascular Physician Branch of Chinese Medical Doctor Association, Expert Consensus Working Group on Management of Hyperkalemia in Patients with Heart Failure in China. Expert consensus on management of hyperkalemia in patients with heart failure in China. Chin J Med 2021; 101 (42):3451-8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20210624-01430. (Chinese) |
| 17. | Chinese Medical Doctor Association Heart Failure Professional Committee, National Cardiovascular Expert Committee Heart Failure Professional Committee, Chinese Journal of Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathy Editorial Board. Expert consensus on ion management for patients with heart failure in China. Chin J HF CM 2020; 4(1): 16-31. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn101460-20200114-00004. (Chinese) |
| 18. | Expert Group of Nephrology Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on serum potassium management practice in patients with chronic kidney disease in China. Chin J Nephrol 2020; 36 (10): 781-92. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441217-20200721-00139. (Chinese) |
| 19. | Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int 2024, 105(Suppl 4S): S117-S314. |
| 20. | 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure. Circulation. 2022; 145:e895-e1032. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001063 |
| 21. | Zhang J, He X, Wu J. The impact of hyperkalemia on mortality and healthcare resource utilization among patients with chronic kidney disease: a matched cohort study in China. Front Public Health 2022; 10: 855395. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.855395. |
| 22. | Expert Group of Guidelines on the Management of Hyperkalemia in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients in China. Guideline on the management of hyperkalemia in maintenance hemodialysis patients in China. Chin J Blood Purif 2022; 21(Suppl): S1-S16. (Chinese) |
| 23. | Xue C, Mei C. Long-term management of hyperkalemia in chronic kidney disease. Chin J Nephrol. 2021, 37(4): 380-4. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441217-20200623-00056. (Chinese) |
| 24. | Dalkey N, Helmer O. An experimental application of the Delphi method to the use of experts. Management Sci 1963; 9: 458-67. |
| 25. |
Diamond IR, Grant RC, Feldman BM, et al. Defining consensus: a systematic review recommends methodologic criteria for reporting of Delphi studies. J Clin Epidemiol 2014; 67(4): 401-9.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.12.002 pmid: 24581294 |
| 26. | Jing X, Xu L, Qin W, et al. The willingness for downward referral and its influencing factors: a cross-sectional study among older adults in Shandong, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020; 17(1): 369. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17010369. |
| 27. | Xiao Y, Chen X, Li Q, et al. Towards Healthy China 2030: modeling health care accessibility with patient referral. Soc Sci Med 2021; 276: 113834. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.113834. |
| 28. | Bernier-Jean A, Wong G, Saglimbene V, et al. Dietary potassium intake and all-cause mortality in adults treated with hemodialysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2021; 16: 1851-61. doi: 10.2215/CJN.08360621. |
| 29. | Yuan Lu, Bi-Cheng Liu & Hong Liu. An evaluation of sodium zirconium cyclosilicate: a new treatment option for hyperkalemia in China. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2023; doi: 10.1080/14656566.2022.2161884 |
| 30. |
Brown R, Bratton SL, Cabana MD, et al. Physician asthma education program improves outcomes for children of low-income families. Chest 2004; 126(2): 369-74. doi: 10.1378/chest.126.2.369.
pmid: 15302719 |
| 31. |
Silva-Cardoso J, Brito D, Frazão JM, et al. Management of RAASi-associated hyperkalemia in patients with cardiovascular disease. Heart Fail Rev 2021; 26(4): 891-6. doi: 10.1007/s10741-020-10069-3.
pmid: 33599908 |
| 32. |
Burton JO, Coats AJS, Kovesdy CP, et al. An international Delphi consensus regarding best practice recommendations for hyperkalaemia across the cardiorenal spectrum. Eur J Heart Fail 2022; 24(9): 1467-77. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2612.
pmid: 35791065 |
| [1] | Sheng-li Liu, Lu-wei Zhang, Jun Tian*. Pseudohyperkalemia with Myelofibrosis after Splenectomy [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2016, 31(4): 258-260. |
| [2] | Hong-min Zhang, Da-wei Liu, Xiao-ting Wang, Yun Long, Quan-hui Yang. Respiratory and Cardiac Characteristics of ICU Patients Aged 90 Years and Older: A Report of 12 Cases [J]. Chinese Medical Sciences Journal, 2016, 31(1): 37-42. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
|